Various expressions of wood
No two pieces of natural wood have the same grain. Even pieces of the same wood species will differ in terms of color shade and grain characteristics. Hida Sangyo uses wood, a precious forest resource, and considers "speckles," "knots and leaf knots," and "heartwood and sapwood" to be unique features of natural wood, and uses them in its products.
We ask for your understanding that these are evidence of the unique character of natural wood, and also for the protection of forests.
Furthermore, the appearance and characteristics vary depending on the wood species. Please check the characteristics of each wood species and choose the one that suits you best.
Tiger stripes
Among wood grains, the most decorative and beautiful ones are called moku (figure). A typical example is the tiger stripe that appears on white oak. This pattern appears only on straight-grained wood, and is highly valued as a lustrous silver grain. The tiger stripe is a cellular tissue that played a role in storing nutrients when the tree was standing. Although it is often mistaken for poor quality wood, moku is not only a natural wood, but also a sign that it is high-quality wood.


Nodules/Lobes
As a tree grows, it extends branches from the trunk, opens its leaves, and stores nutrients. As it grows, small branches fall off and are replaced by larger branches, leaving behind knots, which are the cores of the branches, within the trunk. As the trunk grows, knots move inward from the surface, and when the tree is sawn, they become visible on the surface. These knots are called "small knots" and "leaf knots," and they also become visible on the surface during processing after sawing. Traditionally, materials with knots were not used for furniture, but Hida Sangyo sees knots as a unique feature and makes effective use of them.


Material Shading
Even within a single log, the color of the central part of the trunk (heartwood/red wood) and the part closer to the bark (sapwood/sapwood) vary, so the product may have different shades of color. Heartwood generally refers to the darker part of the interior of the wood, but depending on the tree species, it may be difficult to distinguish by color. It is more resistant to decay and stronger than sapwood, and is also called "reddish/red thick." Sapwood is the part that grows on the periphery of the wood, closer to the bark. It is lighter in color and softer than heartwood, and has more moisture, so it is slightly less resistant to decay.
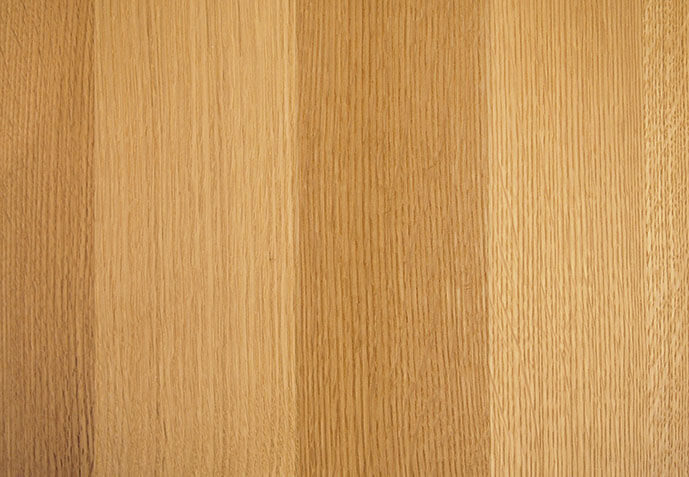
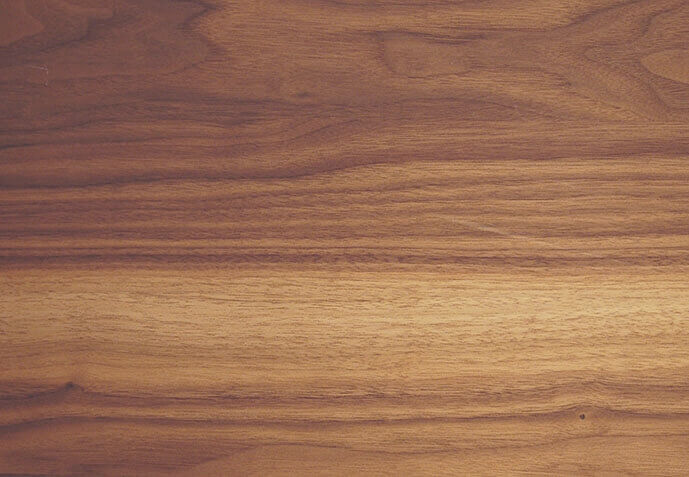


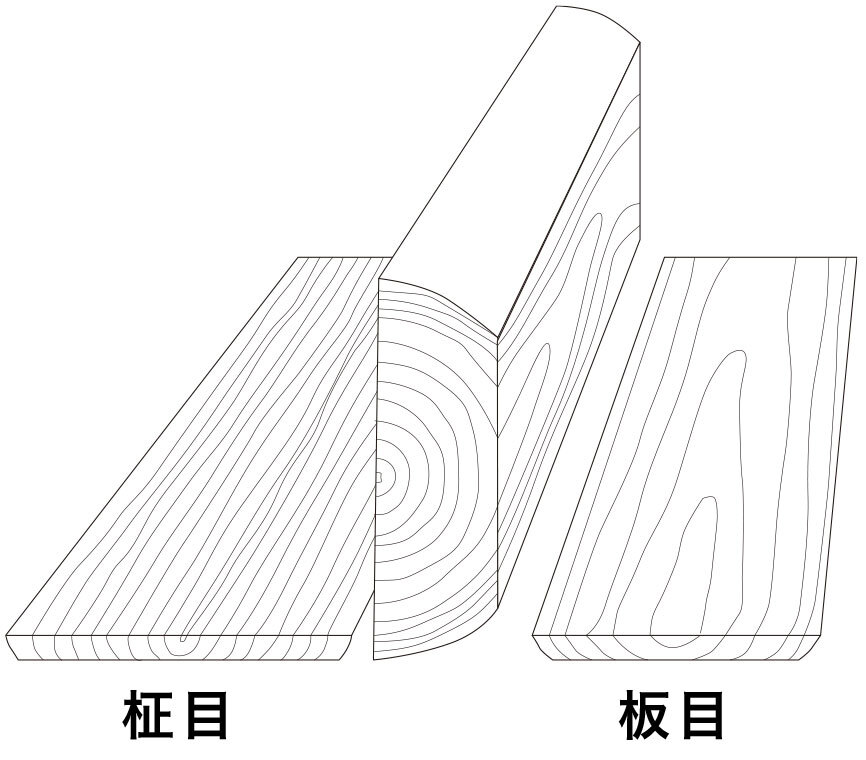
Flat grain and straight grain
Flat grain is wood grain where the annual rings appear in a mountain or bamboo shoot shape. Flat grain can also have various appearances depending on the sawing method, and appears when the log is sawn away from the center.
Straight grain is wood grain where the annual rings are parallel and straight. It appears when the log is cut towards the center.
source: Hida Sangyo Co., Ltd.
